

Please make sure to replace this file by a symlink to avoid incorrect or misleading mount(8) output. etc/mtab is not a symlink or not pointing to /proc/self/mounts. Systemd prints the following warning on boot: To boot under systemd by default, edit /etc/default/grub and change the following line: GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="quiet splash init=/lib/systemd/systemd"Īfter modifying any grub related configuration files like /etc/default/grub the following command is needed to bring the changes into effect. Note that the systemd binary resides now in /lib/systemd/ and /bin/systemd is just a symlink to it. To boot under systemd, the following argument must be specified on the kernel command line: This results in systemd being installed alongside upstart.Īfter installation, the machine will still boot under upstart by default.
#UBUNTU NFS MANAGER INSTALL#
apt-get install systemd libpam-systemd systemd-ui Systemd can be installed from the PPA as follows.
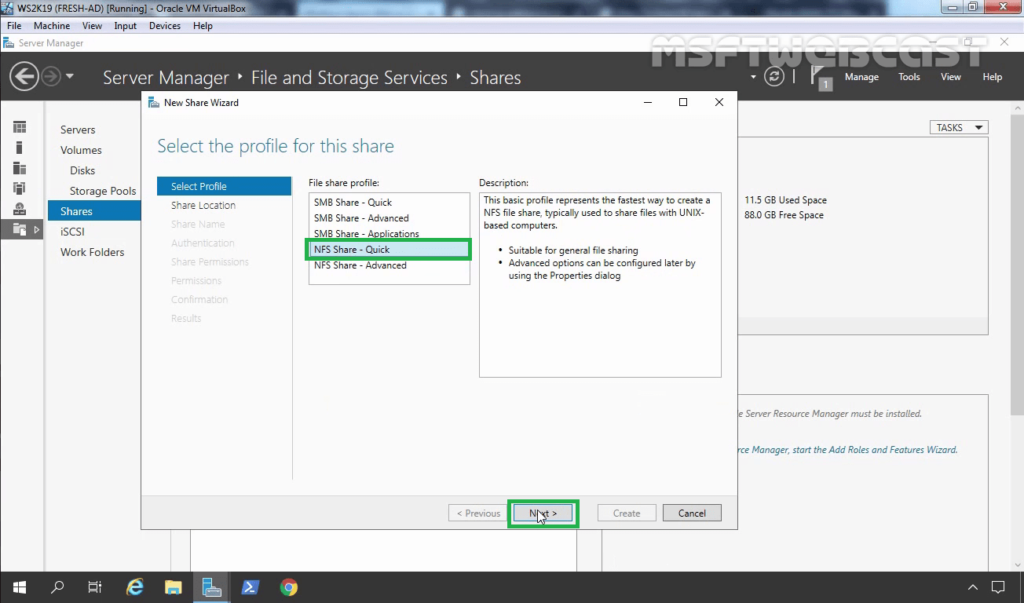
#UBUNTU NFS MANAGER SOFTWARE#
Systemd and related packages are available on this PPA To use the PPA, first add it to your software sources list as follows.
#UBUNTU NFS MANAGER FULL#
If you are installing systemd on a system containing data that you care about, please take a full backup first, and make a plan for restoring from backup in the event that the system ends up unbootable. a virtual machine that you can easily re-install or delete afterwards). If you want to quickly try out systemd, it may be a good idea to create a "sandpit" system for the purpose (e.g. Even if you rely on forums etc, you will probably have to reproduce problems on a standard Ubuntu build before anyone can help you much. If you have a commercial support agreement then installing systemd would almost certainly invalidate it. Installing systemd in Ubuntu may limit the amount of help and support available to you.
If you want to help it's best to be running 15.04. Systemd is under active development in Ubuntu although the rough plan would be to default to systemd during development of 15.04. See the systemd home page for further information.

systemd provides aggressive parallelization capabilities, uses socket and D-Bus activation for starting services, offers on-demand starting of daemons, keeps track of processes using Linux cgroups, supports snapshotting and restoring of the system state, maintains mount and automount points and implements an elaborate transactional dependency-based service control logic. Systemd is a system and session manager for Linux, compatible with SysV and LSB init scripts.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
